Renewable Fuel Standard (RFS) saved more than 1.2 billion metric tons of greenhouse gas emissions

Our most recent study GHG Emissions Reductions due to the RFS 2 – A 2022 update confirms the RFS has resulted in aggregate GHG reductions from the use of biofuels that exceed the EPA’s original projections.
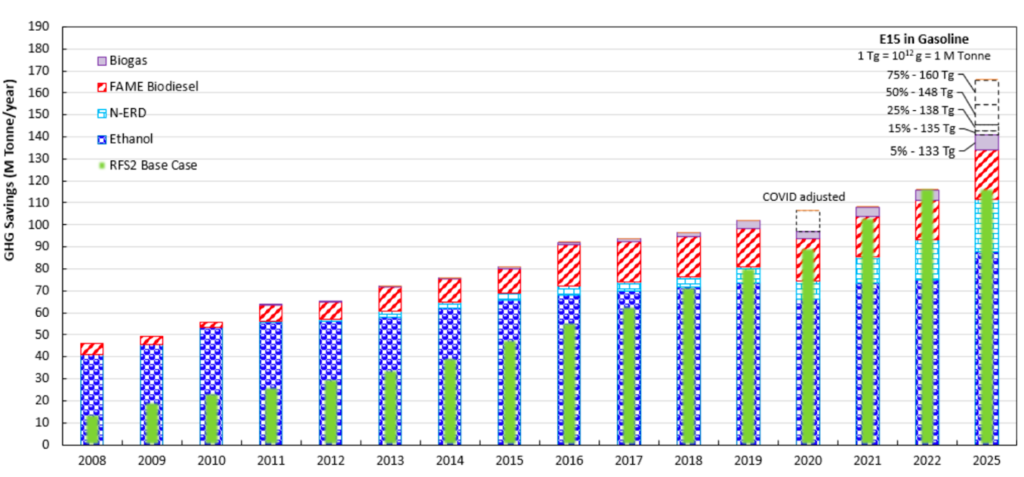
We estimate that the RFS has resulted in 1.2 billion metric tons of cumulative CO2 savings.
GHG reductions from the use of biofuels have exceeded EPA’s projections for the RFS2 base case over the past 15 years. New and expanded pathway’s are forecasted to drive this trend through 2025.
The GHG reductions are due to continuous technology investments reducing the carbon intensity (CI) for corn ethanol and other biofuels. Further savings resulted from higher uptake of corn fiber ethanol, increases in low CI Renewable Natural Gas (RNG), and growth in Non-Ester Renewable Diesel (NERD).
2022 annual emissions savings exceeded pre-COVID levels as fuel demand recovered and technology investments expanded. These significant cumulative savings occurred even though cellulosic biofuels have not met the RFS2 production targets.
The results of our analysis were featured in the Ethanol Producer Magazine. The Renewable Fuels Association commissioned the study for their comments on the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency’s proposed renewable volume obligations for 2023-2025.
Our company works with clients around the world to reduce harmful emissions and negative impacts on the environment and climate. We specialize in life cycle greenhouse gas emission analysis of fuel and energy production pathways with extensive use of the GREET, GTAP and LEM models.
Life Cycle Associates work includes modification of the CA GREET model, developing initial pathway documents for the LCFS, supporting fuel pathways under the LCFS, RFS2, and EU Renewable Energy Directive (RED), and determining applicability of Inflation Reduction Act (IRA) provisions.
Contact us, if you would like to learn more about our services.